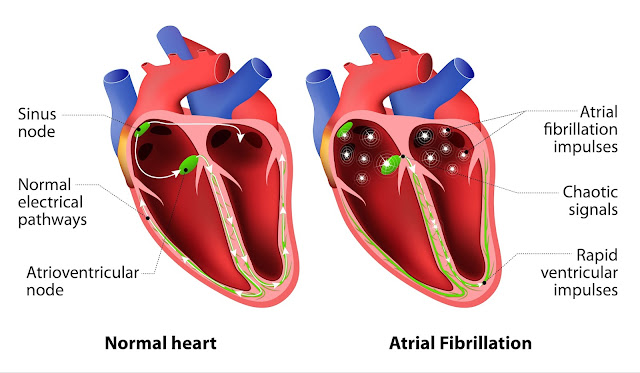
When
the normal heart rate disappears, an arrhythmia occurs. The atrial fibrillation
(AF) is the most common arrhythmia that happens when under normal conditions.
The
heart rate is the speed at which the heart beats; That is, the number of times
it contracts per minute. Normally, the frequency is between 60 and 100 beats
per minute. An arrhythmia occurs when, under normal conditions, the heart rate
goes down (bradycardia) or rises (tachycardia).
The
heart rate stops being regular. Heart rate refers to how the heart beats;
whether they are regular or irregular. The heart rate adapts to the needs of
the body at all times. That's why it speeds up when you exercise and slows down
when you sleep. But, under normal conditions, it should be regular.
Atrial Fibrillation Causes
Occasionally,
atrial fibrillation appears for no apparent reason, but other times there is a
clear trigger. These are the most common causes:
- Hypertension - The most common cause of atrial fibrillation is high blood or hypertension.
- Heart problems - Any disease in the heart (of the valves, angina pectoris, infarction, etc.) can cause atrial fibrillation.
- Hormonal conditions - In some cases, it may be a result of thyroid or other hormonal disorders.
- Unknown - When no cause is found after the necessary tests, atrial fibrillation is called as idiopathic Risks associated.
The
risk of atrial fibrillation increases with age. Usually, atrial fibrillation
occurs in people with previous heart disease. The heart disorders that are
associated with the more frequent occurrence of atrial fibrillation are:
Hypertensive
cardiovascular disease, heart disease due to a chronic increase in blood
pressure which is an excessive strain on the heart muscle.
Diseases
of the heart valves that separate the different chambers of the heart. For
example, mitral stenosis (narrowing) or mitral insufficiency.
An
acute myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease, caused by insufficient
supply of blood to the heart.
A
heart failure or weakness of the heart muscle.
Have
undergone heart surgery.
Inflammation
of the heart muscle (myocarditis) or the membrane surrounding the heart
(pericarditis).
Atrial fibrillation also arises by
extra cardiac causes:
The
excessive drinking. It usually gives short-duration atrial fibrillation. It can
occur after a weekend where you consume excessive alcohol which is called as holiday
heart syndrome or Saturday night heart).
The
consumption of drugs such as cocaine or amphetamines that stimulate the heart.
Heart Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
Treatment
for atrial fibrillation (AF) depends on the severity or frequency of the
symptoms and whether you already have heart disease. General treatment options include medications, medical procedures, and lifestyle changes.
There
are various treatment options available, which are determined to,
Prevent
blood clots from forming and reduce the risk of stroke.
Control
how many times per minute the ventricles contract. This is called frequency
control. Frequency control is necessary because it allows the ventricles enough
time to fill completely with blood. With this approach, irregular heart rhythm
continues, but the person feels better and has fewer symptoms.
Restore
the heart to a normal rhythm. It is called rhythm control. Rhythm control
allows the atria and ventricles to work together again to pump blood to the
body efficiently.
Treat
any underlying disorder that causes or increases the risk of the condition, for
example, hyperthyroidism.
For medical treatment advice, Visit: http://www.healthopinion.net/